The importance of septic systems cannot be overstated. These underground wastewater treatment structures are a fundamental part of homes not connected to centralized city or county sewer systems.
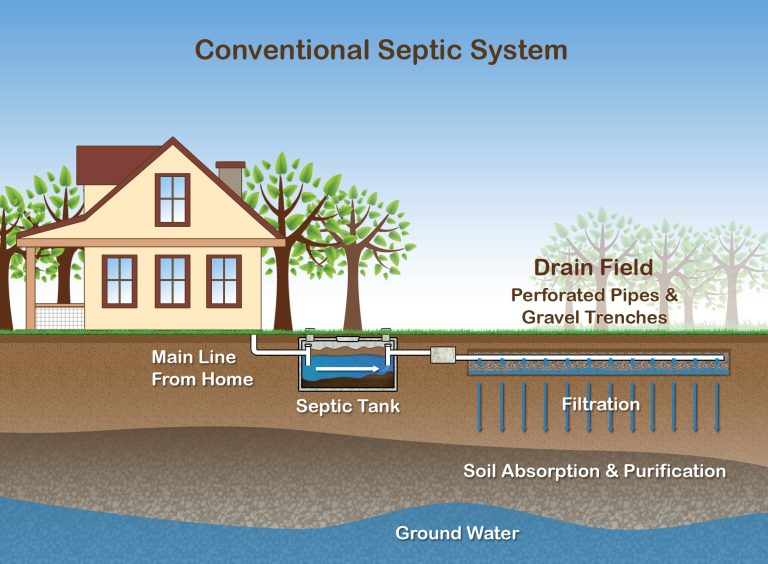
A typical septic system consists of a carefully designed arrangement of components including a septic tank, drain field and soil absorption area. The septic tank is essentially a watertight box crafted from concrete or fiberglass, serving as the first point where wastewater flows from the house.
It holds the wastewater long enough to allow solids to settle down forming sludge, while oil and grease float to the top as scum. Between these two layers lies relatively clear water which then flows into the drainfield for further treatment in the soil.
Complementing this process is an elaborate network of perforated pipes laid in gravel-filled trenches (drainfield) in the soil. This subsystem disperses the liquid from the tank into pits or trenches where it percolates into adjacent soil for final treatment and disposal.
The Paramount Importance of Regular Maintenance
Maintenance does not merely constitute an obligation accompanying ownership; it is integral in prolonging your system’s lifespan and maintaining its efficiency. Consistent maintenance practices aid in early detection of emerging problems, thereby mitigating costs associated with major repairs or total system replacement.
Beyond just cost implications, regular maintenance helps maintain site hygiene by preventing unsightly surface water ponding and foul smells often associated with failed systems. Importantly, it safeguards groundwater quality by limiting direct contamination caused by untreated domestic sewage rich in disease-causing germs.
More so, regular maintenance can prove invaluable when planning home improvements that increase water use (like adding rooms or installing new plumbing fixtures). It can help you determine whether your system has sufficient capacity to handle additional demand, thus averting potential system failures.
Risks Associated with Improper Maintenance
An improperly maintained septic system poses grave dangers. One of its most damaging impacts is the pollution of nearby rivers, lakes and even groundwater used for drinking.
Untreated domestic sewage contains pathogens that can cause diseases such as dysentery, hepatitis and others associated with waterborne pathogens. On a less catastrophic but equally important note, ignoring maintenance can lead to a decline in property value.
A well-functioning septic system is an integral part of home value assessment; a failed or failing one can significantly deter potential buyers. Furthermore, replacing a poorly maintained system could cost thousands of dollars – money that could have been saved through regular simple maintenance routines.
In extreme cases, neglecting regular maintenance can lead to total system failure which often requires expensive repairs or replacement. More than just monetary considerations however, a failed system creates hazardous living conditions which may render your home inhabitable – an inconvenience nobody wishes to face.
Demystifying the Septic System: A Layman’s Guide to Understanding
Basic Components of a Septic System
To truly comprehend septic maintenance and circumvent any detrimental DIY faux pas, we must first explore its anatomy. The prime components include a septic tank, a drainfield or leach field, and the soil absorption area.
The septic tank, typically constructed of concrete or plastic, is buried underground as the receptacle for waste materials from your home. It is here in this subterranean container where solid waste begins its decomposition journey.
Notably, these tanks are designed to prevent leakage into the surrounding environment which underscores their integral role in environmental protection. Drainfields or leach fields then take center stage as liquid waste exits the septic tank.
The drainfield is an intricate network of perforated pipes laid in gravel-filled trenches or beds. Its primary function is to dispense wastewater into the soil hence acting as an organic filter against harmful particles and organisms.
We come upon what could be termed as nature’s final purification gate – the soil absorption area. This area creates a natural barrier against pollutants reaching our groundwater supplies by filtering out any remaining impurities from the wastewater before it percolates further into the earth.
The Inner Workings of a Septic System: A Silent Symphony
Peeling back another layer in our quest for understanding brings us face to face with how exactly a septic system operates and treats wastewater – a process akin to conducting an unseen symphony. The first movement commences with all household wastewater funneling into the septic tank through an inlet pipe.
In this relatively quiet setting, solid materials descend forming sludge at bottom while lighter materials like oil and grease float atop creating scum – both layers embarking on their decomposition dance led by bacteria. Next comes an interlude, where the liquid waste or ‘effluent’ in between the sludge and scum layers, exits to the drainfield via an outlet pipe marking the transition to the second movement.
The drainfield then disperses this effluent into the soil for further treatment. The finale unfolds in the soil absorption area, where any remaining harmful substances and pathogens are removed as clean water percolates down into groundwater.
The Role of Bacteria: Nature’s Cleanup Crew
Bacteria play a pivotal role within septic systems, becoming micro-stewards of waste breakdown. Primarily anaerobic bacteria, which thrive in environments devoid of oxygen, initiate breaking down solid matter in the septic tank.
These bacterial maestros act on organic materials in wastewater transforming solids into liquids and gases. This biological activity reduces volume and prevents tank overflow – a testament to their indispensable function.
Understanding your septic system is not merely about being acquainted with its components or mechanics but also appreciating its silent symphony conducted by nature itself through bacteria. It is by acknowledging this harmonious interplay that we can contribute effectively towards its maintenance.
Common DIY Septic Maintenance Mistakes
The Perils of Ignoring Regular Inspections
The practice of regular septic system inspections is an essential aspect of maintaining the health and functionality of your septic system. These inspections should ideally be carried out at least once every three years for a primary tank, and annually for systems with mechanical components. The reasons behind this regularity are manifold, as these examinations allow for the early detection of potential problems before they spiral into costly repairs.
An inspection involves a thorough analysis of all parts of the system including the tank, drainfield, and associated pipework. Experienced inspectors will examine the scum and sludge layers in your tank to determine whether it’s time for a pump out or not.
Additionally, they’ll check drains in your house to verify if waste is flowing smoothly into your tank. When regular inspections are overlooked, homeowners run the risk of exacerbating minor issues that could have been easily rectified if caught on time.
These can compound into catastrophic failures that necessitate extensive repairs or even an entire system replacement. Moreover, neglected tanks often overflow leading to groundwater contamination which could pose serious health risks.
The Importance and Implications of Pumping Your Tank Regularly
Akin to oil changes for vehicles or filter replacements in HVAC systems, pumping out your septic tank serves as its routine maintenance task – one that should be undertaken every three to five years dependent on usage volume and household size. This action depletes accumulated solid waste material which if allowed to amass unchecked can cause significant damage including blockages or overflows. Pumping frequency should ideally depend on four major factors: The size of your household, total wastewater generated, volume of solids in the wastewater (which in turn depends on whether you use a garbage disposal), and the size of your septic tank.
A system that is not pumped regularly enough will likely lead to solids being pushed into the drainfield, causing clogging and premature failure. Failure to pump your septic tank regularly can lead to the build-up of sludge and scum beyond its capacity.
This often results in a backflow into the household plumbing system causing toilets, sinks, and drains to overflow. Additionally, an excess of solid waste in the tank may cause solids to enter and block your drainfield or even contaminate local water bodies.
The Consequences of Misusing Household Water
Misuse of household water is yet another common error made by homeowners while maintaining their septic systems. Unrestricted excessive water usage puts undue pressure on your system; every time you flush an additional gallon down the drain, your septic system must work extra hard to filter and decompose this waste.
Moreover, using a substantial volume of water in a condensed timeframe leads to hydraulic overloading. This occurs when more water is sent through the system than it can handle which forces solid waste out into the distribution box or leach field leading to clogs or overflows.
It’s recommended that homeowners stagger their use of heavy water fixtures like washing machines or dishwashers throughout each day. Equally damaging is disposing non-biodegradable items such as feminine hygiene products, wipes (even those labeled as “flushable”), diapers or chemicals down drains.
These items don’t break down easily if at all within a septic tank thus occupying valuable space and potentially blocking flow within pipes leading from your home to your tank. They can also kill beneficial bacteria in tanks which are crucial for breaking down solid waste material.
Specific DIY Mistakes to Avoid
Driving or parking over the Drainfield: Weight Pressure and Its Consequences
The drainfield, also known as a leach field, forms a crucial part of your septic system. It serves as the final step in the treatment process where the wastewater is returned to the soil. A common but highly detrimental mistake homeowners commit involves driving or parking vehicles over this crucial area.
Your drainfield is not designed to withstand significant weight pressure. When you drive or park vehicles over it, it could potentially lead to compacted soil and crushed pipes.
Compacted soil hinders proper absorption of wastewater into the environment, rendering your system inefficient. Additionally, crushed pipes disrupt normal flow of waste material leading to backups and overflow incidents.
The long-term effects on your soil absorption area can be devastating and costly. The absurption quality of your soil may be permanently reduced while crushed pipes necessitate expensive repairs or even replacement of your entire septic system in severe cases.
Miscalculations in Landscaping: Planting Trees near Your Drainfield
While trees add aesthetic value to your property and contribute positively towards an eco-friendly environment, planting them near your septic drainfield is an error fraught with potential perils for any homeowner. Tree roots naturally grow towards areas with higher water concentration – a virtue that can turn into a vice when it comes to septic systems.
In their quest for moisture and nutrients, tree roots are capable of infiltrating pipes within the system causing blockages or even rupturing them completely. To avoid such adverse scenarios from unfolding, one must ensure that they adopt appropriate landscaping measures around their septic system by being mindful about what they plant near it.
Opt for plants with shallow root systems like grasses or flowering perennials. These vegetation types will not only enhance your property’s beauty but also prevent unnecessary damage to your septic system.
Overstepping DIY Boundaries: Opening a Septic Tank Alone
While being proactive and hands-on about maintaining your septic system is laudable, there are certain tasks that require professional handling due to the inherent risks they pose. Take for instance, opening a septic tank.
It might seem like an easy DIY task, but it can be perilous if not executed with the proper expertise. Opening a septic tank without appropriate safety gear or knowledge can expose you to harmful gases and bacteria contained within these systems.
Hydrogen sulfide and methane are among the toxic gases generated in septic tanks that can cause serious health issues ranging from nausea to even loss of consciousness in more severe cases. Hence, for such intricate tasks, it is highly recommended to seek professional help.
Professionals are equipped with both the technical know-how and specialized tools necessary for safely performing such operations while adhering to regulatory standards. This ensures your well-being as well as the optimal functioning of your system.
Advantages and Limitations of DIY Septic Maintenance
Seeking Balance Between Independence and Expertise
DIY septic maintenance is an enticing prospect for homeowners with a desire to be hands-on in the care and upkeep of their homes, offering cost savings, a sense of self-reliance, and an intimate understanding of the property’s systems. However, the intricate nature of septic systems necessitates caution. It’s important not to be overzealous in your personal involvement; there are elements that should ideally be left to professionals due to safety hazards or complex requirements.
The advantages of DIY maintenance can’t be understated. Regular checks can help identify potential issues before they escalate into expensive repairs or replacements.
Moreover, by adopting responsible household practices such as efficient water usage or proper waste disposal, you contribute substantially towards the longevity of your system. Despite these advantages, there are also limitations that mustn’t be ignored.
A lack of professional training can lead to mistakes with severe consequences for both your home and environment. Even minor errors in septic system maintenance can result in polluted local water sources or unpleasant back-ups in the home.
Cost
The Financial Implications: A Closer Look
Now we delve deeper into one of the most significant factors influencing decisions on septic system maintenance: cost. DIY approaches often seem attractive due to apparent immediate savings; avoiding call-out charges for professionals can reduce outlay substantially.
Yet financial concerns extend beyond initial costs; one must also consider long-term economic implications. Mistakes made during DIY maintenance may necessitate expensive repairs down the line.
Additionally, poorly maintained systems have shorter lifespans leading to premature replacement needs. Conversely though, a well-maintained system is an economically sound investment that boosts your property value significantly while offering peace of mind about future repair costs.
Conclusion
Striking the Perfect Balance
It’s clear that DIY septic maintenance holds both promise and peril. The trick lies in striking a balance between personal involvement and professional intervention, ultimately creating a harmony that allows you to enjoy the benefits of self-reliance without compromising on system integrity or safety.
So, equip yourself with knowledge, stay cautious where necessary, embrace the satisfaction of hands-on involvement where possible, and lastly, don’t hesitate to seek professional expertise when the situation demands it. Informed decisions will not only safeguard your home but also ensure a clean and healthy environment for years to come.